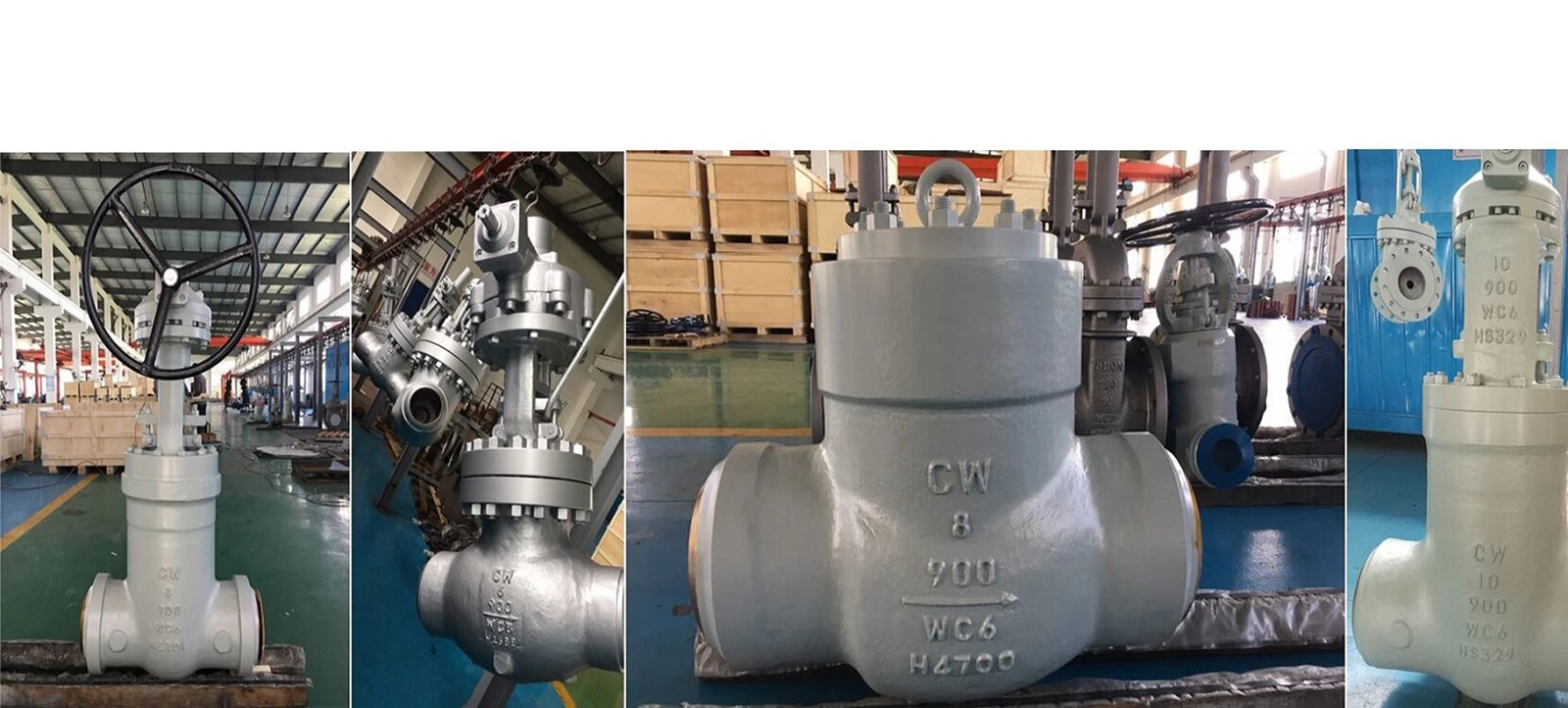
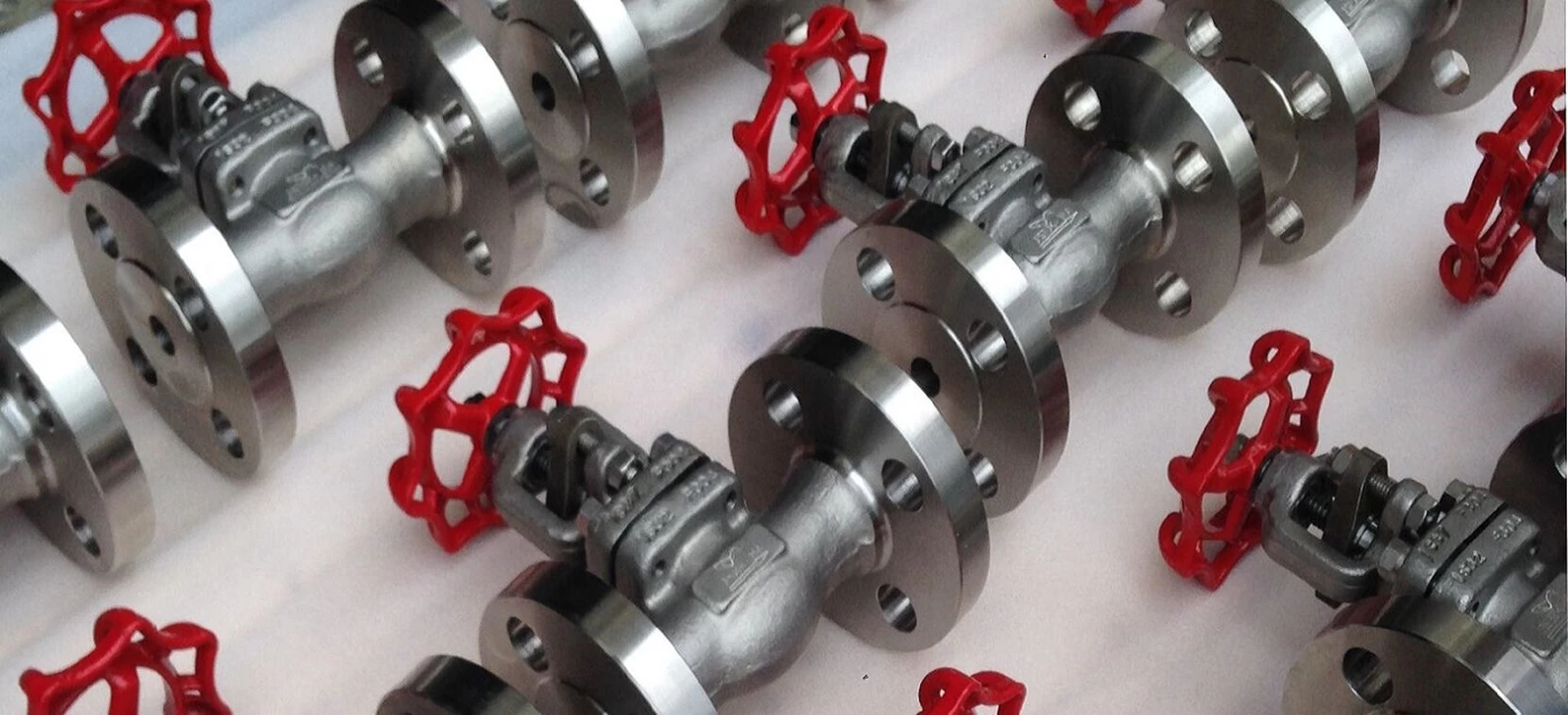
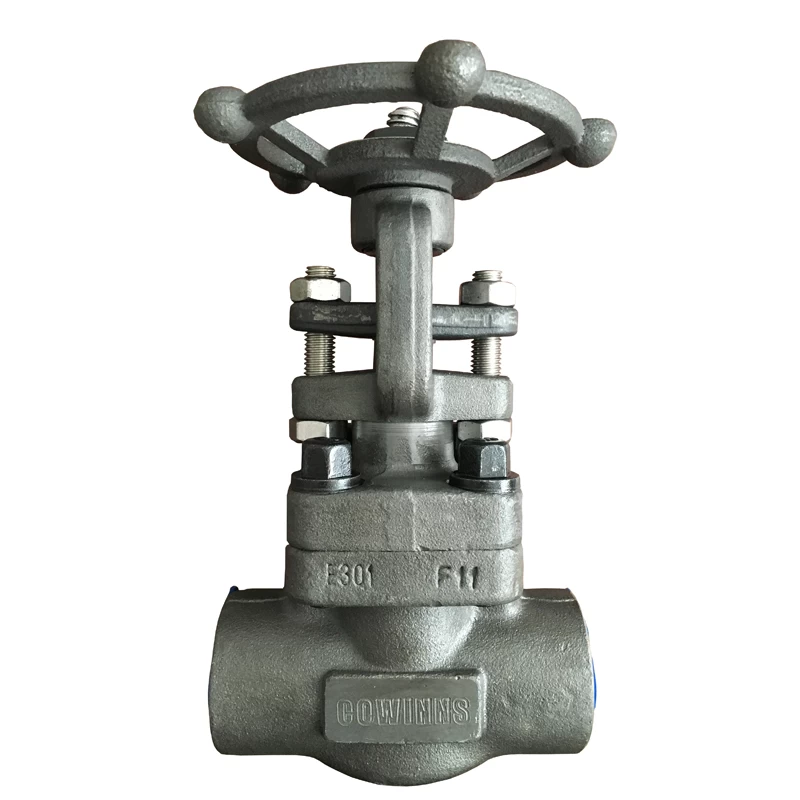
Cowinns control valve engineers design various control valves for power plant applications. Based on several years of experience, we have won numerous new power plant projects and OEM orders. We can supply not only complete control valves but also OEM machining for control valve cages, plugs, and seats. Cowinns has a strong advantage in precision parts machining, which helps our clients save significant costs. If you have potential requirements, please feel free to email us.

Control valve cage

Control valve cage
Here share some knowledge for control valve
Control valve is a key parts for industrial application. In the field of industrial automation process control, it accepts the control signal output by the adjustment control unit and uses power operation to change the final control element of process parameters such as medium flow, pressure, temperature, and liquid level. Generally composed of actuators and valves. According to the characteristics of the stroke, the control valve can be divided into straight stroke and angular stroke; according to the power used by the actuator, it can be divided into three types: pneumatic control valve, electric control valve, and hydraulic control valve; according to their functions and characteristics There are three types of linear characteristics, equal percentage characteristics and parabolic characteristics. The regulating valve is suitable for air, water, steam, various corrosive media, mud, oil and other media. Commonly used classification of control valves: pneumatic control valve, electric control valve, hydraulic control valve, self-operated control valve.
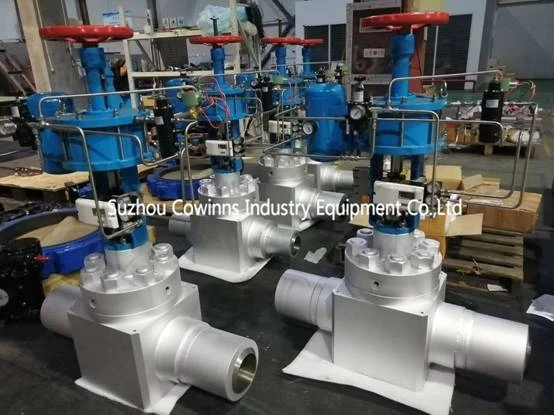

In the automatic control of modern factories, regulating valves play a crucial role. The production process in these factories depends on the precise distribution and control of the flowing medium. Whether the control involves energy exchange, pressure reduction, or simple container feeding, specific final control elements are required to achieve it.
A regulating valve acts as a variable resistance in the pipeline. It alters the turbulence of the process fluid or creates a pressure drop in the case of laminar flow. This pressure drop is caused by changing the valve resistance, or “friction,” a process commonly referred to as throttling. For gases, the process is approximately isothermal or adiabatic, with deviations depending on the gas's non-ideality (Joule-Thomson effect). For liquids, the pressure drop results from turbulent flow or viscous friction, both of which convert pressure into heat, causing a slight temperature increase.
A typical control loop consists of three main components. The first is a sensing element, usually a transmitter, which measures the process parameters to be controlled, such as pressure, liquid level, or temperature. The transmitter’s output is sent to the regulator, which calculates the deviation between the desired setpoint and the actual process value, then sends correction signals to the final control element—the regulating valve. The valve adjusts the fluid flow to bring the process parameters to the desired values.
Regulating valves belong to the series of control valves. Their primary function is to adjust the pressure, flow, temperature, and other parameters of the medium, serving as the final control element in the process control loop.
 +86 512 68781993
+86 512 68781993