Boiler Terminology Explanations (Part 3)
Boiler Terminology Explanations (Part 3)
21. Superheated Steam
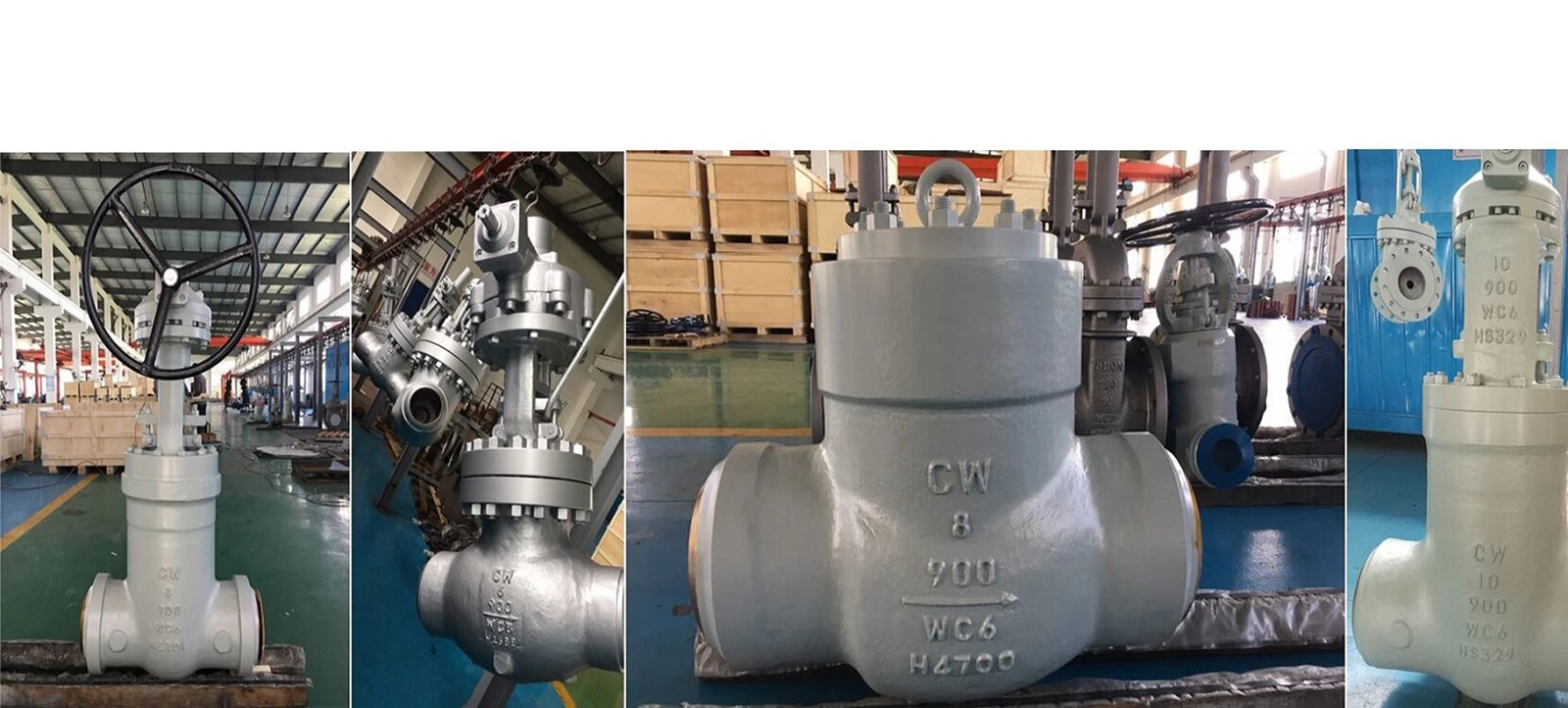
Steam whose temperature is higher than the corresponding saturation temperature at a given pressure is called superheated steam.Cowinns high temperature gate valve can be used for boiler pipeline.
22. Degree of Superheat
The temperature difference between superheated steam and the corresponding saturation temperature at the same pressure is called the degree of superheat.
23. Latent Heat of Vaporization
The amount of heat required to convert 1 kg of saturated water into 1 kg of saturated steam is called the latent heat of vaporization or latent heat.
24. Dryness Fraction
The mass percentage of dry saturated steam in wet steam is called the dryness fraction.
25. Moisture Content
The mass percentage of saturated water in wet steam is called the moisture content.
26. Critical Point
As pressure increases, the difference between saturated water and dry saturated steam becomes smaller. When the pressure reaches a certain value, there is no distinction between saturated water and dry saturated steam, and they share the same state parameters. This point is called the critical point.
27. Isochoric Process (Constant Volume Process)
In a constant volume process, the pressure of a gas is proportional to its absolute temperature, i.e., P₁/T₁ = P₂/T₂. In this process, all the heat added to the gas is used to increase its internal energy.
28. Isobaric Process (Constant Pressure Process)
A process that occurs at constant pressure is called an isobaric process, such as water vaporization in a boiler or steam condensation in a condenser. In an isobaric process, specific volume is proportional to temperature, i.e., v₁/T₁ = v₂/T₂. When temperature decreases, gas is compressed, and specific volume decreases; when temperature increases, gas expands, and specific volume increases. The heat added in an isobaric process is equal to the enthalpy difference between the final and initial states. The T-S curve of this process is a logarithmic curve with a positive slope.
29. Isothermal Process (Constant Temperature Process)
A process that occurs at constant temperature. The relationship P₁v₁ = P₂v₂ = constant holds, meaning that all the heat added to the system is converted into work done by the gas, and all the work done on the gas is transformed into heat released to the surroundings.
30. Adiabatic Process
A process in which no heat exchange occurs with the external environment is called an adiabatic process, also known as an isentropic process. In thermal machines such as steam turbines and gas turbines, insulation materials are used to minimize heat loss. Additionally, the working fluid expands so rapidly that there is no time for significant heat dissipation, making the process approximately adiabatic.

 +86 512 68781993
+86 512 68781993