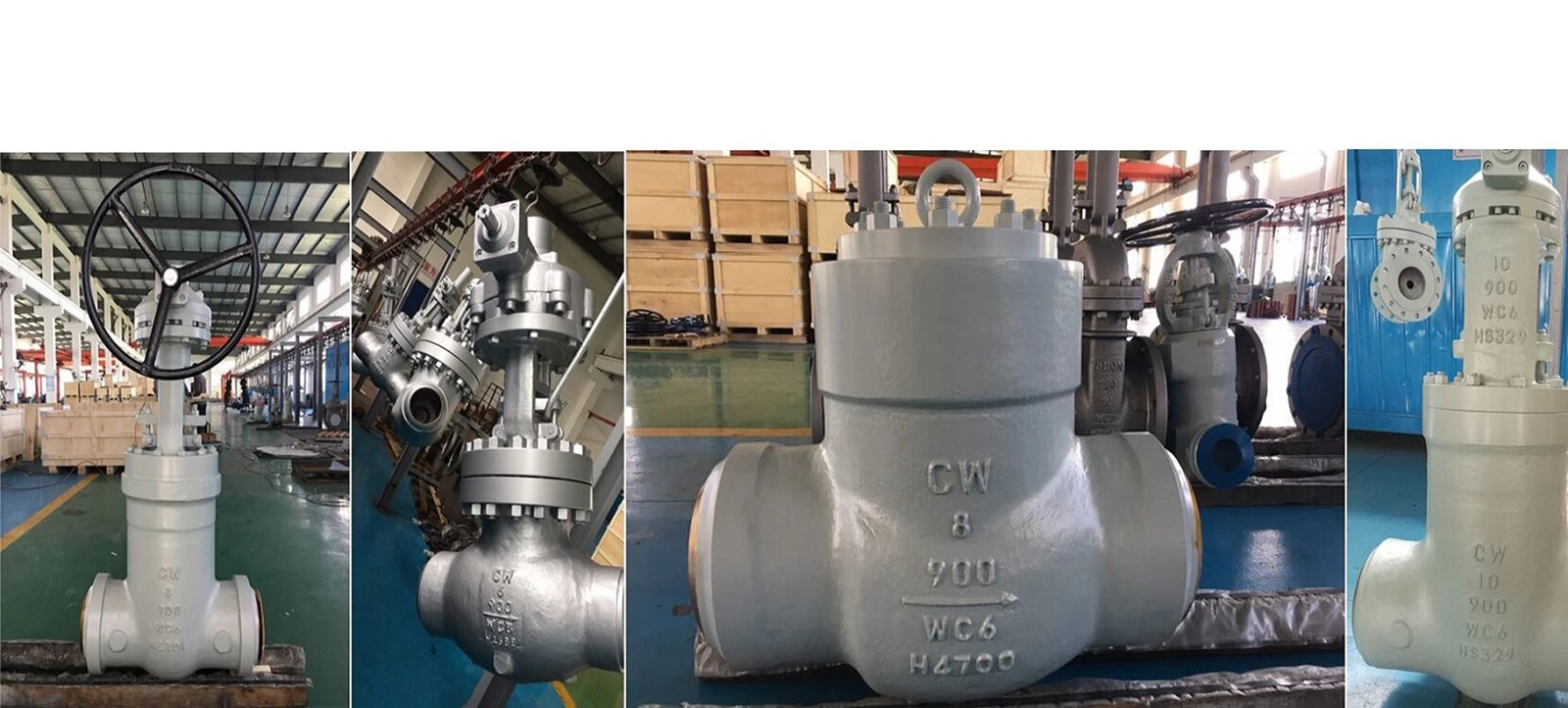
14 contraindications for valve installation and troubleshooting
A valve is a device used to control the direction, pressure, and flow of a fluid in a fluid system. It is a device that allows the medium (liquid, gas, powder) in piping and equipment to flow or stop and can control its flow. In the construction process, the way the valve is installed will directly affect the normal operation in the future. This article will summarize some precautions when installing the valve.
Taboo 1: The main materials, equipment and products used in construction lack technical quality appraisal documents or product qualification certificates that meet the current standards issued by the State or the Ministry.
Consequences: The quality of the project is unqualified, there is a hidden danger of the accident, and it cannot be delivered and used on time, and must be reworked for repair; resulting in the delay of the construction period and the increase in labor and material input.
Measures: The main materials, equipment and products used in the water supply and drainage and heating and sanitation projects should have technical quality appraisal documents or product certifications that comply with the current standards issued by the country or the ministry; they should indicate their product names, models, specifications, and national quality standards Code, date of manufacture, name and location of manufacturer, product inspection certificate or code.

Taboo 2: Before the valve is installed, the necessary quality inspection is not carried out according to the regulations.
Consequences: During the system operation, the valve switch is not flexible, the closing is not strict, and the phenomenon of water leakage (steam) occurs, which causes rework and repair, and even affects the normal water supply (steam).
Measures: Before the valve is installed, the pressure strength and tightness test should be done. The test shall be conducted with 10% of each batch (same brand, same specification, same model) quantity, and not less than one. For the closed-circuit valves installed on the main pipe to cut off, the strength and tightness test shall be carried out one by one. The valve strength and tightness test pressure shall comply with the provisions of "Code for Construction Quality Acceptance of Building Water Supply, Drainage and Heating Engineering" (GB 50242-2002).
Taboo 3: The specifications and models of the installed valves do not meet the design requirements. For example, the nominal pressure of the valve is less than the system test pressure; the gate valve is used when the diameter of the water supply branch pipe is less than or equal to 50mm; the cut-off valve is used for the dry and riser pipes of hot water heating; and the butterfly valve is used for the suction pipe of the fire pump.
Consequences: affecting the normal opening and closing of the valve and adjusting the resistance, pressure and other functions. It even caused damage to the valve and forced repairs during system operation.
Measures: Familiar with the application scope of various valves, select the valve specifications and models according to the design requirements. The nominal pressure of the valve should meet the requirements of the system test pressure. According to the requirements of the construction specifications: the water supply branch pipe diameter is less than or equal to 50mm should be used globe valve; when the pipe diameter is greater than 50mm should be used gate valve. Gate valves should be used for hot water heating dry and vertical control valves, and butterfly valves should not be used for the suction pipes of fire pumps.

Taboo 4: The valve installation method is wrong. For example, the flow direction of the water (steam) of the globe valve or check valve is opposite to the mark, the valve stem is installed downward, the horizontally installed check valve is installed vertically, and there is no open or closed space for the open stem gate valve or butterfly valve handle. Not facing the inspection door.
Consequences: Valve failure, difficulty in overhauling the switch, and the valve stem facing down often causes water leakage.
Measures: Install in strict accordance with the valve installation instructions. The open stem gate valve has enough stem to extend the opening height. The butterfly valve fully considers the rotation space of the handle. Various stems should not be lower than the horizontal position, let alone downward. Concealed valves should not only be equipped with inspection doors that meet the opening and closing needs of the valves, but also the valve stem should face the inspection doors.
Taboo 5: Ordinary valve flanges for butterfly valve flanges, especially for triple off set butterfly valve
Consequences: The size of the butterfly valve flange and the common valve flange are different, and some flanges have a small inner diameter, and the valve flap of the butterfly valve is large, causing the valve to fail to open or hard to open and damage the valve.
Measures: The flange should be processed according to the actual size of the butterfly valve flange.
Taboo 6: No holes or embedded parts are reserved in the construction of the building structure, or the size of the reserved holes is small and the embedded parts are not marked.
Consequences: During the construction of the heating and sanitation project, cutting the building structure and even cutting off the stressed steel bars will affect the safety performance of the building.
Measures: Seriously familiar with the construction drawings of the heating and sanitation project, according to the needs of the installation of pipelines and support hangers, actively and carefully cooperate with the construction of the construction structure to reserve holes and embedded parts, specifically refer to the design requirements and construction specifications.
Taboo 7: When the pipeline is welded, the misalignment of the pipe after the alignment is not on a center line, there is no gap between the alignment, the thick-walled pipe is not shoveled, and the width and height of the weld do not meet the requirements of the construction specifications.
Consequences: The misalignment of the pipe does not directly affect the welding quality and the perception quality in the center line. There is no gap at the mouth, thick wall pipe does not shovel the groove, and the width and height of the weld do not meet the requirements. The welding cannot reach the strength requirements.
Measures: After welding the pipe to the butt, the pipe should not be misaligned. The center should be on the center line, and the gap should be left. The thick wall pipe should be shoveled. In addition, the width and height of the weld should be welded according to the specifications.
Taboo 8: The pipeline is buried directly on the frozen soil and untreated loose soil. The spacing and position of the pipeline piers are improper, even in the form of dry yard bricks.
Consequences: Due to the unstable support, the pipeline was damaged during the backfilling process, resulting in rework and repair.
Measures: The pipeline should not be buried in frozen soil and untreated loose soil. The spacing of the piers must meet the requirements of the construction specifications. The supporting pads must be firm, especially at the pipeline interface, and should not bear shear forces. Brick piers shall be built with cement mortar to ensure integrity and firmness.
Taboo 9: The material of the expansion bolts used to fix the pipe bracket is inferior, the diameter of the expansion bolts installed is too large, or the expansion bolts are installed on brick walls or even lightweight walls.
Consequences: The pipe support is loose, the pipe is deformed or even falls off.
Measures: Qualified products must be selected for the expansion bolts. If necessary, samples should be taken for testing and inspection. The diameter of the expansion bolts should not be greater than the outer diameter of the expansion bolts by 2 mm.

Taboo 10: The flange and gasket of the pipeline connection are not strong enough, and the connection bolt is short or thin in diameter. Rubber pads are used for thermal pipes, asbestos pads are used for cold water pipes, and double-layer pads or bevel pads are used.
Consequences: The flange joint is not tight, even damaged, and there is leakage. Flange gasket protruding into the pipe will increase the resistance of water flow.
Measures: Flanges and gaskets for pipelines must meet the requirements of pipeline design working pressure. Flange gaskets for heating and hot water supply pipes should be rubber asbestos pads; flange gaskets for water supply and drainage pipes should be rubber pads. The gasket of the flange shall not protrude into the pipe, and its outer circle is suitable to the flange bolt hole. No bevel pad or several gaskets should be placed in the middle of the flange. The bolt diameter of the connecting flange should be less than 2mm than the flange aperture. The length of the bolt rod protruding nut should be 1/2 of the nut thickness.
Taboo 11: During the hydraulic pressure strength test and the tightness test of the pipeline system, only the pressure value and water level changes are observed, and the leakage inspection is not enough.
Consequences: Leakage occurs after the pipeline system is in operation, affecting normal use.
Measures: When the pipeline system is tested according to the design requirements and construction specifications, in addition to recording the pressure value or water level changes within the specified time, it is especially necessary to carefully check whether there is a leakage problem.
Taboo 12: Sewage, rainwater, and condensate pipes are concealed without water-closure tests.
Consequences: It may cause water leakage and user losses.
Measures: The water shut-off test should be checked and accepted in strict accordance with the specifications. Underground installation, suspended ceiling, pipe room and other concealed sewage, rainwater, condensate pipes, etc. should be ensured to ensure no leakage.
Taboo 13: The pipeline system is not carefully flushed before completion, and the flow rate and speed cannot meet the pipeline flushing requirements. Even the flushing is replaced by the hydraulic pressure test drain.
Consequences: The water quality does not meet the requirements for the operation of the pipeline system, which often results in the reduction or blockage of the pipeline section or valve section especially for metal to metal seat butterfly valve. This kindly butterfly seat surface should be protected more carefully.
Measures: Flush with the maximum set juice flow in the system or a water flow speed not less than 3m / s. The color and transparency of the outlet water and the water color and transparency of the inlet water should be the same by visual inspection.

Taboo 14: Water pressure test under negative temperature during winter construction.
Consequences: As the tube quickly freezes during the hydrostatic test, the tube freezes.
Measures: Try to carry out the water pressure test before winter application, and blow the water after the pressure test, especially the water in the valve must be cleared, otherwise the valve will freeze and crack. The project must be carried out under the water pressure test in winter, and the indoor positive temperature should be maintained, and the water should be blown off after the pressure test. When the hydraulic test is not available, compressed air can be used for testing.
 +86 512 68781993
+86 512 68781993