The difference between gauge pressure, absolute pressure and vacuum
The difference between gauge pressure, absolute pressure and vacuum
In industrial production processes, valves and gauges are normal components in the piple line.Chemical operators and instrument maintenance personnel need to master the concepts of different pressures.Especially for high pressure pipeline such as pressure seal gate valve.
The concepts of absolute pressure, gauge pressure and vacuum
Absolute pressure, or true pressure, is the pressure calculated from absolute zero pressure. Or the pressure calculated from vacuum, absolute pressure, referred to as absolute pressure.
Gage pressure, referred to as gauge pressure, refers to the pressure calculated from the local atmospheric pressure at that time. When the pressure of the measured system is equal to the local atmospheric pressure at that time, the pointer of the pressure gauge points to zero. That is, the gauge pressure is zero.
Vacuum, when the absolute pressure of the measured system is less than the local atmospheric pressure at that time, the difference between the local atmospheric pressure and the absolute pressure of the system is called vacuum. The pressure measuring instrument used at this time is called a vacuum gauge.
The relationship between absolute pressure, gauge pressure and vacuum is shown in the figure:
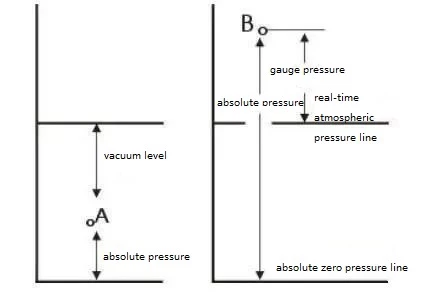
The Relationship Between Absolute Pressure, Gauge Pressure, and Vacuum Level
A- The pressure at the pressure measuring point is less than the atmospheric pressure at that time
B- The pressure at the pressure measuring point is greater than the atmospheric pressure at that time

Pressure gauge
The difference between gauge pressure, absolute pressure and differential pressure
Absolute pressure is absolute pressure (the engineering term, the physics term is absolute pressure); differential pressure is the pressure difference (or pressure difference), that is: absolute pressure-atmospheric pressure=gauge pressure.
"Gauge pressure" in the vacuum industry specifically refers to: the relative pressure value of the gas measured by an ordinary vacuum gauge (relative pressure gauge), expressed as a negative number, which refers to the difference between the measured gas pressure and the atmospheric pressure. It is also called negative pressure.

vacuum gauge
The so-called "vacuum" refers to the gas state in a given space with a pressure lower than 101325 Pascal (that is, a standard atmospheric pressure of about 101KPa).
There are usually two ways to mark the vacuum degree:
One is to mark it with "absolute pressure" and "absolute vacuum" (i.e. how much higher the pressure is than the "theoretical vacuum");
In actual situations, the absolute pressure value of the vacuum pump is between 0 and 101.325KPa. The absolute pressure value needs to be measured with an absolute pressure instrument. At 20℃ and altitude = 0, the initial value of the instrument used to measure the vacuum degree (absolute vacuum gauge) is 101.325KPa (i.e. one standard atmospheric pressure).
The second is to mark it with "relative pressure" and "relative vacuum" (i.e. how much lower the pressure is than the "atmospheric pressure").
"Relative vacuum" refers to the difference between the pressure of the object being measured and the atmospheric pressure at the measurement location. Measured with an ordinary vacuum gauge. In the absence of vacuum (i.e. normal pressure), the initial value of the gauge is 0. When measuring vacuum, its value is between 0 and -101.325KPa (usually expressed as a negative number).
For example, if the measurement value of a micro vacuum pump PH2506B is -75KPa, it means that the pump can draw a vacuum state that is 75KPa lower than the atmospheric pressure at the measurement location.
 +86 512 68781993
+86 512 68781993